PDCA cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act) is an iterative four-phases management method for continually improving processes, products or services and for resolving problems. In this article we dig a bit deeper into the critical steps of this PDCA process. Learn how to keep the momentum flowing with continuous improvement, while enlisting the help of a PDCA cycle in your business today.
PDCA is based on the scientific method of problem-solving and was popularized by Dr W. Edwards Deming, who is considered by many to be the father of modern quality control. PDCA is an integral part of lean management (Kaizen). The PDCA cycle is also known as: the Deming Wheel, Shewhart Cycle or Deming Cycle.
The PDCA framework can improve any process or product by breaking it into smaller steps. The model can be used in all sorts of business environments; new product development, project and change management, product lifecycle, supply chain management, etc.
It is proven effective for:
- Exploring a range of solutions to problems
- Planning data collection and analysis in order to verify and prioritize problems or root causes
- Working towards continuous improvement
- Avoiding wastage of resources
- Helping to implement Total Quality Management
- Implementing any change
- Fostering teamwork through brainstorming and problem-solving

The four phases that comprises the PDCA cycle can be repeated over and over as part of a never-ending cycle of continual learning and improvement. The PDCA phases are:
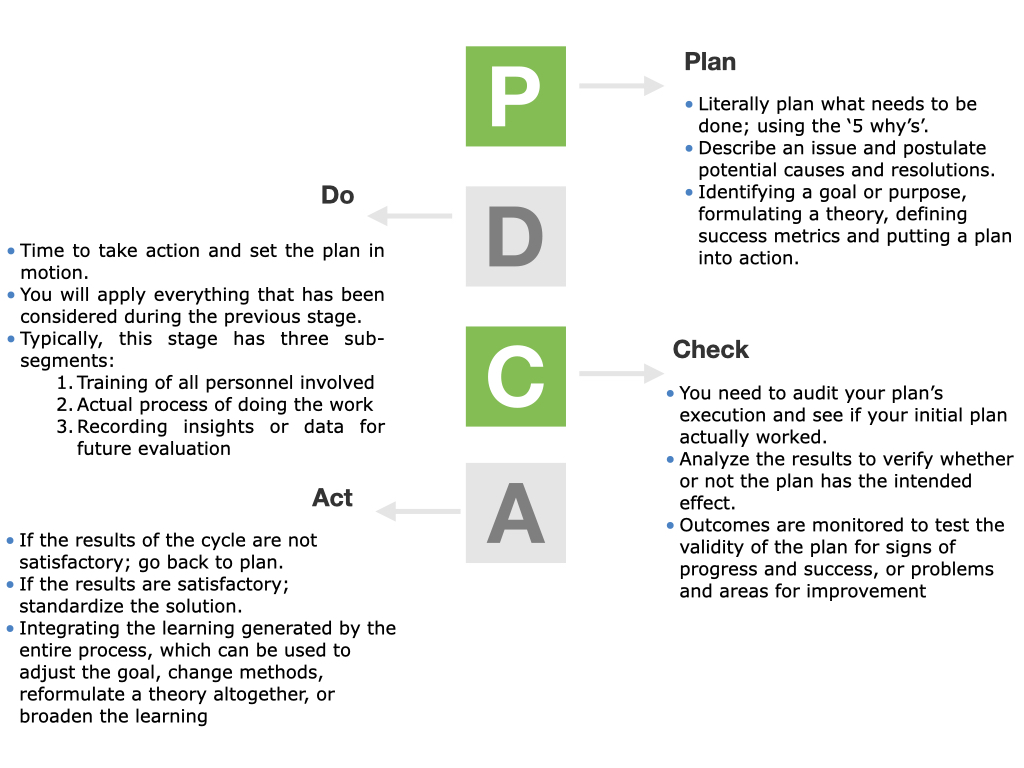
PDCA brings in continuous change, it is implemented in a manner that the process is modified and made adept at cost reduction, profit maximization and increased satisfaction. As the environment today is dynamic in every possible manner, there is a need for updating the techniques and processes as frequently as possible.
Here you can find an example of a PDCA cycle for improvement of the quality management system in medical laboratory according to the ISO 9001:2015 standards. The cycle is focused on the organization context and the stakeholders’ requirements. All the phases are leadership-dependent, and they consider the “risk-based thinking” in all the decisions.
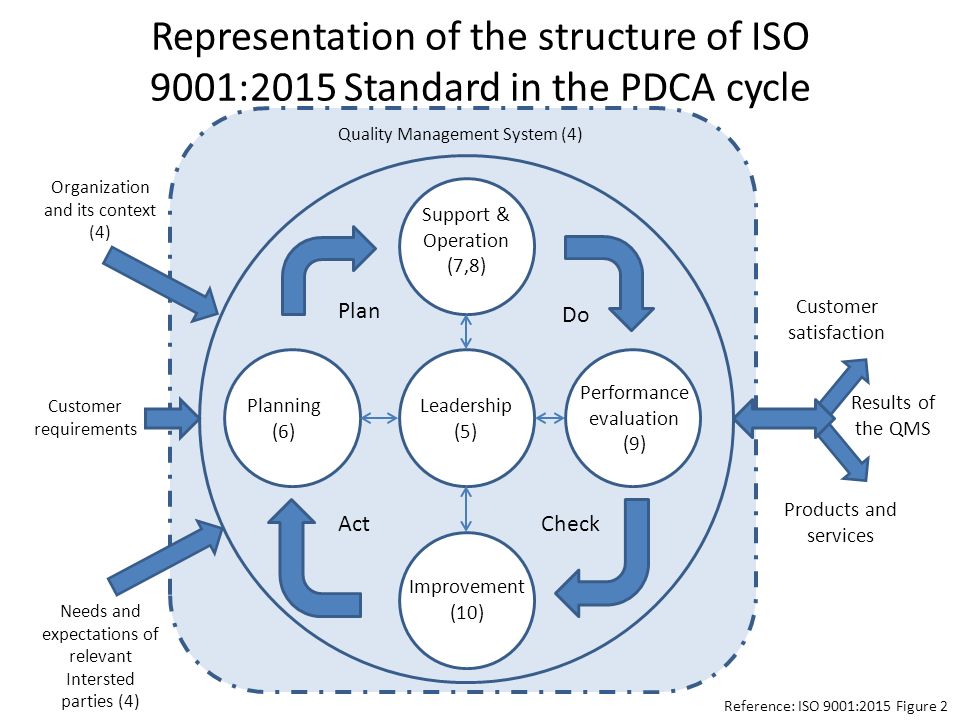
In conclusion, the PDCA process provides a continuous loop of planning, doing, checking and acting. The iterative process of the PDCA cycle enables and promotes a continuous improvement and continuous learning culture. It provides a comprehensive and effective approach for solving problems and managing change.
To find out more about how Pinnaql can help move you along your quality journey, contact us today.
Sources
http://www.westgard.com/iso-9001-2015-requirements.htm
https://deming.org/explore/p-d-s-a
